Vitamin D for Coronavirus … and Much More
- Joan Rothchild Hardin

- May 3, 2020
- 10 min read
Updated: Nov 17, 2024
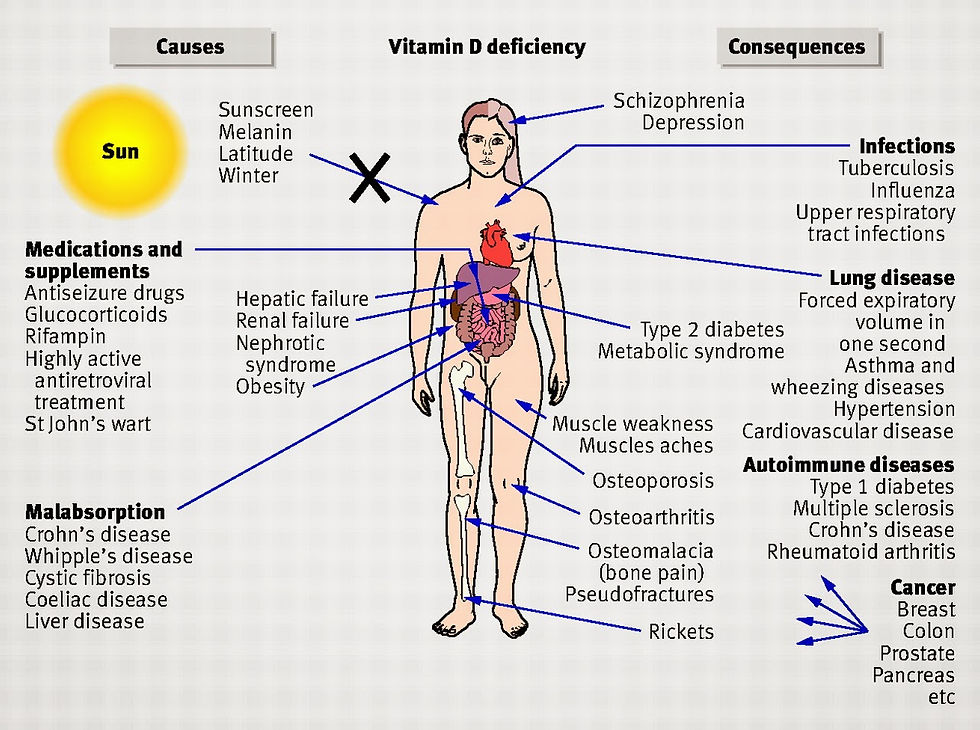
Results from a recent data review by English scientists link COVID-19 incidence and deaths across Europe to Vitamin D deficiency. A good blood serum level of Vitamin D is needed for healthy immune functioning – including fighting off Coronavirus-19. Unfortunately, most of us are severely Vitamin D deficient.
“When your skin is exposed to sunlight, it makes vitamin D from cholesterol. The sun’s ultraviolet B (UVB) rays hit cholesterol in the skin cells, providing the energy for vitamin D synthesis to occur. The sun’s ultraviolet B (UVB) rays hit cholesterol in the skin cells, providing the energy for vitamin D synthesis to occur.” So you might want to rethink using sunscreen. “…Some studies estimate that sunscreen of SPF 30 or more reduces vitamin D production in the body by about 95–98%.” (Raman, 2018)
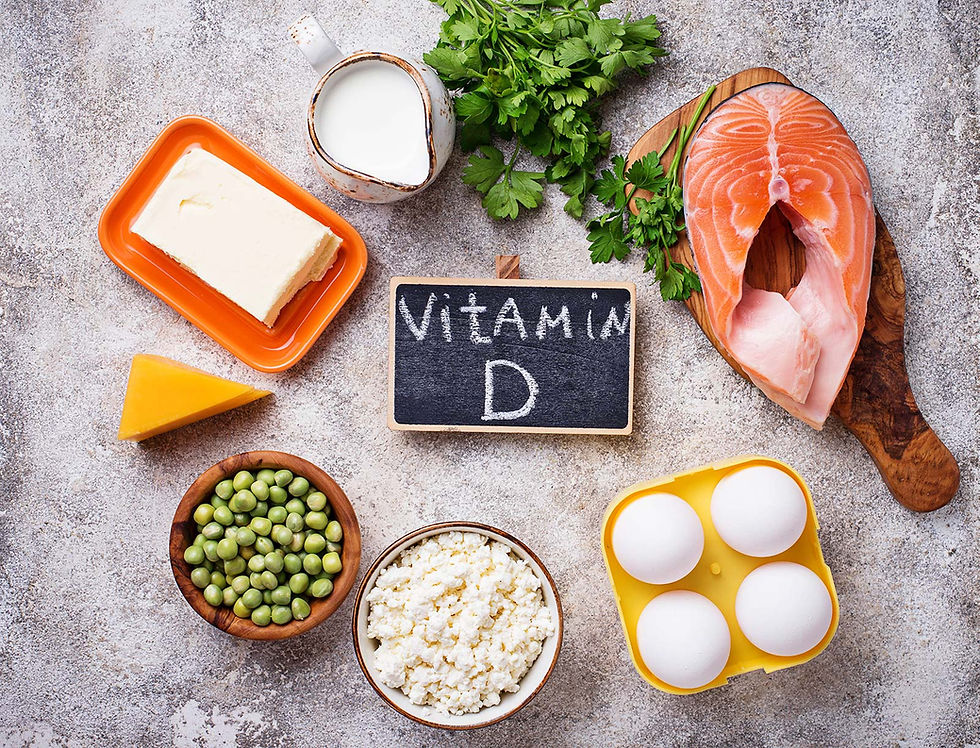
There are also dietary sources of Vitamin D: Salmon, tuna, mackerel, sardines, cod liver oil, egg yolks, cheeses, butter, shiitake and button mushrooms, sunflower seeds and sprouts, and high quality supplements.

MOST OF US ARE VITAMIN D DEFICIENT
An adequate blood serum level Vitamin D is vitally important for healthy immune functioning. Unfortunately, most of us are severely Vitamin D deficient.
Unlike other vitamins the body needs, Vitamin D functions like a hormone, “and every single cell in your body has a receptor for it.” (Spritzler, 2018)
Having a sufficient Vitamin D blood level is essential for maintaining good health and preventing a wide range of autoimmune and neurological diseases: Type 1 and 2 diabetes, asthma, allergies, cancer, Alzheimer’s, MS, susceptibility to infection (including viral respiratory infections) among them. (Hardin, 8/28/2015)
“Vitamin D deficiency is very common. It’s estimated that about 1 billion people worldwide have low levels of the vitamin in their blood. According to a 2011 study, 41.6% of adults in the US are deficient. This number goes up to 69.2% in Hispanics and 82.1% in African-Americans. (Spritzler, 2018)
This widespread Vitamin D deficiency is likely contributing to the incidence of Coronavirus-19 and the number of deaths from COVID-19.
COMMON RISK FACTORS FOR VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
Having dark skin
Being elderly
Being overweight or obese
Not eating enough fish or dairy
Living far from the equator where there is little sun year-round
Always using sunscreen when going out
Staying indoors
– Spritzler, 2018
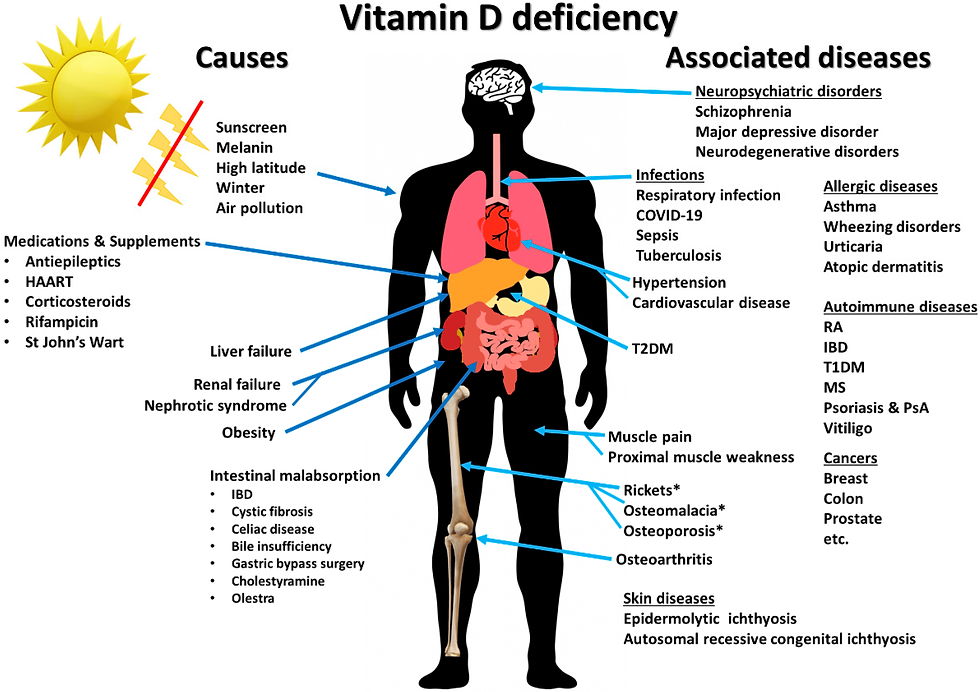
SIGNS & SYMPTOMS OF VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY
Often becoming ill, especially with colds or flu: A prime role for Vitamin D is keeping your immune system strong so you’re able to fight off viruses and bacteria that cause illness. Vitamin D interacts directly with the cells responsible for fighting infection.
Excessive fatigue or tiredness: Low Vitamin D blood levels can cause fatigue. “A large observational study looked at the relationship between vitamin D and fatigue in young women. The study found that women with blood levels lower than 20 ng/ml or 21–29 ng/ml were more likely to complain of fatigue than those with blood levels over 30 ng/ml.”
Bone and back pain: A study found a relationship between Vitamin D deficiency and chronic back pain in 9,000 older women. Another controlled study found that people deficient in D were nearly twice as likely to have bone pain in their legs, joints or ribs compared to people with normal range blood levels.
Depression: Controlled studies have shown that giving Vitamin D to people who are deficient helps improve depressed mood, including Seasonal Affective Depression.
Impaired wound healing: Vitamin D plays a role in controlling inflammation and fighting infections, both important for proper wound healing. A test tube study suggested that Vitamin D increases the production of compounds crucial for forming new skin during the wound healing process. In an analysis of patients with diabetic foot infections, those with severe D deficiency were more likely to have higher levels of inflammatory markers.
Bone loss: Low bone mineral density may be a sign of Vitamin D deficiency. Getting adequate D is important for preserving bone mass as you age.
Hair loss: Hair loss is often attributed to stress but D deficiency may also be a cause. Alopecia areata, an autoimmune disease characterized by severe hair loss from the head and other parts of the body, is associated with rickets, a disease that causes soft bones in children due to Vitamin D deficiency.
Muscle pain: Muscle pain can have many causes. There is evidence that D deficiency may be a potential cause of muscle pain in children and adults. In a study of 120 children with Vitamin D deficiency who had growing pains, a single dose of Vitamin D reduced pain scores an average of 57%.
– Spritzler, 2018

COVID-19 INFECTION & DEATHS LINKED TO VITAMIN D3 DEFICIENCY
A few weeks ago, three medical researchers in East Anglia, England pre-published their data review testing the hypothesis that Vitamin D3 plays a protective role for SARS-Cov2 infections. They note that “previous studies identified associations between higher levels of ACE2 and better coronavirus disease health outcomes. In the lung, ACE2 protects against acute lung injury…. Vitamin D3 … pronouncedly (creates) enhanced expression of ACE2.”

“The primary aims of this study are to assess if there is any association between the mean levels of vitamin D in various countries and the mortality caused by COVID–19. The secondary aim was to identify if there is any association between the mean vitamin D levels in various countries and the number of cases of COVID–19.”
To limit confounding biases (eg, latitude), they focused on 20 European countries hit by Coronavirus-19. The researchers searched the health literature for the mean levels of vitamin D among the citizens in each country. Then they compared those figures with the numbers of COVID-19 deaths in each country as of 20 March 2020.
The researchers defined severe Vitamin D deficiency as a serum blood level lower than 30 nmol/L. (30 nmol/L = 12 ng/mL – ie, a very serious deficiency. Charts I’ve seen show the deficiency cut off at somewhere between 30-50 ng/mL so 12 ng/mL is very serious.)
The data demonstrated very significant correlations between the mean Vitamin D levels and the number of cases of COVID–19 in each country – as well as between the mean Vitamin D levels and the number of deaths caused by COVID-19 in each country. People with the lowest levels of Vitamin D in their blood were significantly more likely to die from COVID-19 than people with adequate levels. The scientists note that “Vitamin D levels are severely low in the aging population especially in Spain, Italy and Switzerland. This is also the most vulnerable group of population for COVID-19.” Their conclusions: “We believe, that we can advise Vitamin D supplementation to protect against SARS-CoV2 infection.”
– Illie, Stefanescu & Smith, 4/202020
You can see a pre-print of the paper on Research Square. This 4 March 2020 MedCram Lecture video by pulmonologist Roger D. Seheult, MD on Vitamin D3 for Coronavirus-19 prevention is for those of you who want more technical information
RECOMMENDED VITAMIN D INTAKE & BLOOD LEVELS HAVE BEEN TOO LOW
The major circulating form of Vitamin D is considered to be 25-hydroxyvitamin D, measured in ng/mL (nanograms per milliliter). This blood test is currently considered the best indicator of the body’s Vitamin D supply. The reference range for the 25 Hydroxy D Test (also known as 25 (OH)D) is 25-80 ng/mL. (Nguyen 11/20/2019)
There’s Evidence These Vitamin D Blood Level Interpretations Are Too Low for Maintaining Good Health

Many scientists have long argued that setting 30 ng/mL as the dividing line between Vitamin D deficiency and adequacy (as in the commonly used chart above) has been dangerously incorrect. And now the Coronavirus-19 pandemic is apparently proving them correct. This Chart Reflects the Vitamin D Blood Levels Needed for Good Health

From an article on Vitamin D and Health by Dairy Nutrition:
“The evidence to date, largely from systematic reviews, indicates that higher levels of serum 25(OH)D may significantly reduce the risk of several chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, and some cancers, such as breast and colon cancer.
“Research also indicates that increased levels of 25(OH)D are associated with higher bone mineral content in older children and adolescents (6 to 18 years) and higher bone mineral content and bone mineral density in postmenopausal women and elderly men.
“In some studies, higher vitamin D levels are also associated with beneficial immunologic outcomes, such as reduction in risk of acute lower respiratory tract infections. In addition, vitamin D appears to reduce the risk of multiple sclerosis and is likely beneficial in its treatment.” (Dairy Nutrition, undated)
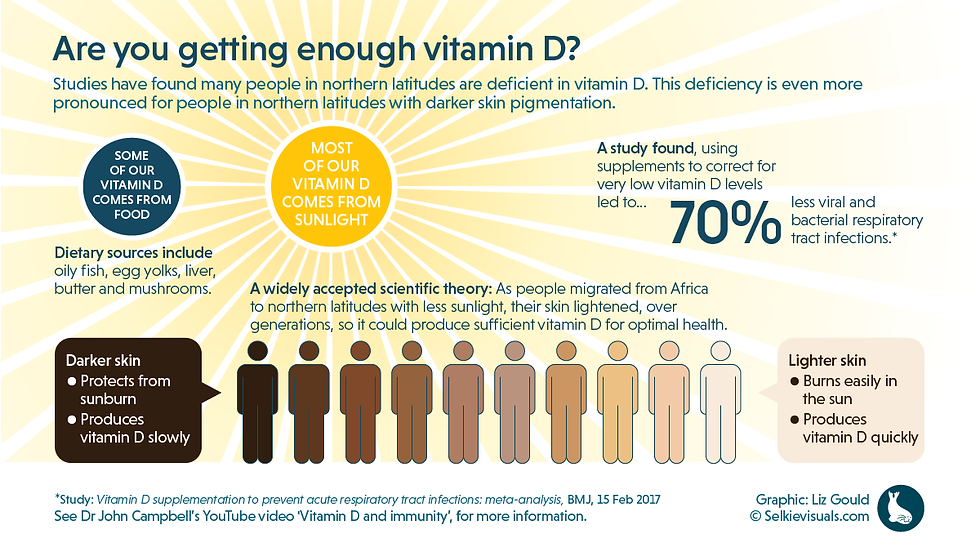
“The Institute of Medicine has placed the recommended dietary allowance, or RDA, for vitamin D at 600 international units (IU) per day for young adults and 800 IU per day for adults older than 70. Other experts suggest that adults’ vitamin D needs are much higher.” (Torborg, 4/25/2017)

A recent recap by Dr Joseph Mercola on the importance of Vitamin D and the dangers of a deficiency. (This particular article is about Vitamin D and sleep):
Vitamin D deficiency has become epidemic in many parts of the world as we’ve been taught to avoid the sun. Lower vitamin D levels have produced two unexpected consequences: poor sleep and a dangerous change in the intestinal microbiome.
Vitamin D is needed to produce acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that helps you get into the deeper, healing phases of sleep, and controls your normal paralysis during deep sleep
Certain B vitamins also play an important role in sleep. For example, B5 — pantothenic acid — makes coenzyme A, which you use to make acetylcholine.
If you’re healthy you have four types of gut bacteria living inside you. Those bacteria need your vitamin D to grow properly, and in return they make eight B vitamins that you need. Without enough vitamin D the healthy bacteria are replaced by others that don’t require vitamin D but are unable to make the B vitamins that you need to sleep normally.
Ideally, you need to normalize your gut microbiome so that your gut bacteria make all the B vitamins your body and brain need.
To normalize your gut microbiome, maintain a vitamin D level over 40 ng/mL and take B50 or B100 (all eight B’s at 100 mg each) for three months (Mercola, 3/1/2020).

Given the current Coronavirus-19 pandemic and also the very high incidence of other diseases influenced by a Vitamin D deficiency, it would be wise to get a 25-hydroxyvitamin to learn your actual blood serum level. If your score is below 50 ng/mL – or you have warning signs of a Vitamin D deficiency, you might want to take a high quality, bio-available Vitamin D3 supplement daily.

SUPPLEMENTAL VITAMIN D3 DOSAGE RECOMMENDATIONS
“Vitamin D3 ensures that calcium is absorbed easily and K2 (MK-7) activates the protein, osteocalcin, which integrates calcium into bone. Without D3 and K2, calcium cannot do its job effectively. Vitamin K2 (MK-7) activates matrix GLA protein (MGP) to bind excess calcium and promote arterial flow and flexibility.” (Better You, 2020)
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that promotes the absorption of calcium, regulates bone growth and is important for immune function. It exists in two main forms: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol – from plants) and Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol – from animals). The skin produces D3 when exposed to sunlight but it’s hard for those of us living farther from the equator to get adequate sun exposure – especially when we use sun screen and cover our skin with clothing.

Ask your doctor to do a 25-hydroxyvitamin test to learn your actual blood serum level. Based on the studies and recommendations above, if your score is below 50 ng/mL – or you have warning signs of a Vitamin D deficiency, you’d be wise to take a high quality, bio-available Vitamin D3 supplement daily for a few months then do a retest. If your repeat test level is 50 ng/mL or higher, you’re probably getting enough D3.

“Dr. Joan Lappe and her colleagues looked prospectively at more than 400 postmenopausal women over a four-year period of time. Women in the study group were given 1100 IU of vitamin D and 1000 mg of calcium daily. The control group did not receive this. Results: Women who took the vitamin D and calcium reduced their rate of cancer by 60%. The authors found that for every 10 ng/ml increase in a woman’s vitamin D blood level, the relative risk of cancer dropped by 35%.”
THE VITAMIN D3 SUPPLEMENT I TAKE
On the recommendation of my Functional Medicine health care providers, and consistent with research I’ve read, I’ve taken a softgel cap containing 5,000 iu of bioavailable Vitamin D3 (Metagenics) every day after breakfast for many years. I also take a capsule containing 150 mcg of K2 MK-7 (Health As It Ought To Be) at the same time. And I frequently eat fatty fish, eggs, butter and mushrooms so am also getting some D3 and D2 from my diet. Spending a lot of time inside an apartment in New York City, I’m pretty sure the amount of D3 I get from sunshine is negligible.
My Vitamin D,25-OH blood level in mid-March was 65 ng/mL. (Reference Range: 30-100 ng/mL) This made me and my doctor very happy. When a virus is going around, I sometimes feel my body fighting it off if I’m also feeling stressed but it hardly ever turns into a full blown case.
If you’re looking for a high quality, non-GMO, gluten-free, soy-free supplement that contains both 5,000 iu Vitamin D3, a balanced amount of K2 MK-7 and some calcium in a single capsule, there’s Dr Mercola’s Vitamin D3 & K2.
“Researchers from UC San Diego discovered that vitamin D levels of 48 ng/mL or higher were linked to a 67 percent reduction in cancer risk when compared to those whose levels were 20 ng/mL or less. Studies have shown that higher sun exposure throughout a women’s lifetime is linked to a 70 percent lower risk of developing breast cancer. In 2018 The British Medical Journal revealed that high vitamin D levels were associated with a reduction in cancer risk of 20 percent when it came to liver cancer. It is also known that ovarian cancer cases were more than three times more likely to have low 25[OH]D levels.” (Sircus, 2019)
For additional information on Vitamin D & how to choose a supplement, see:
“Mayo Clinic: Vitamin D toxicity is rare in people who take supplements, researchers report.” The evidence is clear that vitamin D toxicity is one of the rarest medical conditions and is typically due to intentional or inadvertent intake of extremely high doses,” writes Dr. Hollick, a professor of medicine, physiology and biophysics at Boston University School of Medicine.” (Sircus, 2019)
IMPORTANT NOTE: Your Vitamin D serum level should be monitored with periodic blood tests to make sure it’s high enough to protect your health.
REFERENCES
Better You. (2020). Vitamin D and Vitamin K. See: https://betteryou.com/vitamin-d-vitamin-k
Dairy Nutrition (undated). Vitamin D and Health. See: https://www.dairynutrition.ca/nutrients-in-milk-products/vitamin-d/vitamin-d-and-health
Nguyen, H.C.T. (11/20/2019). Vitamin D3 25-Hydroxyvitamin D. MedScape. See: https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2088694-overview
Hardin, J.R. (1/25/2015). Whole Food Supplements (Bio-available) vs OTC (Synthetic) Vitamins. See: http://allergiesandyourgut.com/2015/01/25/whole-food-supplements-bio-available-vs-otc-synthetic-vitamins/
Hardin, J.R. (11/30/2014). ALZHEIMER’S AND VITAMIN D DEFICIENCY. See: http://allergiesandyourgut.com/2014/11/30/alzheimers-gut-bacteria-music/
Hardin, J.R. (8/28/2015). Prediabetics Have Fewer Gut Bacteria. See: https://allergiesandyourgut.com/2015/08/28/prediabetics-have-fewer-gut-bacteria/
HealthLine. (2020). Vitamin D2 vs. D3: What’s the Difference?. See: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d2-vs-d3
Illie, P.C., Stefanescu, S., & Smith, L. (4/20/2020). The role of Vitamin D in the prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 infection and mortality. See: https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-21211/v1
McRae, M. (5/1/2020). COVID-19 Deaths Are Being Linked to Vitamin D Deficiency. Here’s What That Means. See: https://www.sciencealert.com/covid-deaths-are-being-linked-with-vitamin-d-deficiency-here-s-what-that-means
Mercola, J. (3/1/2020). The Importance of Vitamin D and B5 for Optimal Sleep. See: https://articles.mercola.com/sites/articles/archive/2020/03/01/gominak-vitamin-d.aspx
Raman, R. (4/28/2018). How to Safely Get Vitamin D From Sunlight. HealthLine. See: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-from-sun
Sircus, M. (8/2/2019). Vitamin D Deficiency as a Cause of Diseases & Safe High Dose Vitamin D Treatments. See: https://drsircus.com/cancer/vitamin-d-deficiency-as-a-cause-of-diseases-safe-high-dose-vitamin-d-treatments/#_edn6
Spritzler, F. (7/23/2018). 8 Signs and Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency. HealthLine. See: https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/vitamin-d-deficiency-symptoms
Torborg, L. (4/25/2017). Mayo Clinic. Mayo Clinic Q and A: How much vitamin D do I need? See: https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinic-q-and-a-how-much-vitamin-d-do-i-need/ © Copyright 2020. Joan Rothchild Hardin. All Rights Reserved.
DISCLAIMER: Nothing on this site or blog is intended to provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.


Comments